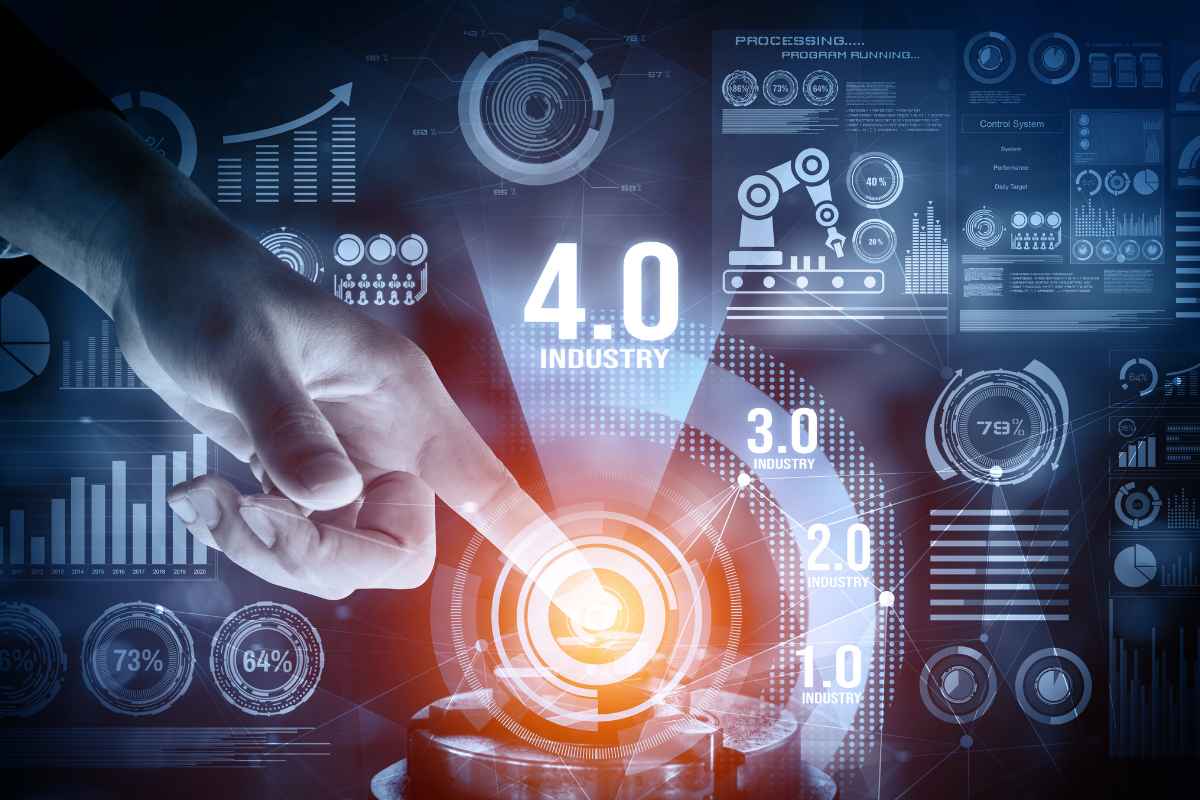
The world is undergoing a technological transformation unlike any seen before, and at the forefront is the rise of Industry 4.0. Characterized by the fusion of digital, physical, and biological systems, this revolution is reshaping industries, optimizing processes, and driving innovation on an unprecedented scale.
What is Industry 4.0?
The term “Industry 4.0” refers to the fourth industrial revolution, which builds on the digital advancements of the third industrial revolution. While the third revolution brought computers and automation into manufacturing, Industry 4.0 takes it a step further by integrating smart technology, AI, robotics, IoT (Internet of Things), and big data into production processes.
Unlike the mechanical steam power of the first industrial revolution or the mass production and assembly lines of the second, the rise of Industry 4.0 focuses on smart, autonomous systems. These systems not only process and analyze data but also communicate and collaborate with each other in real-time, creating a highly efficient and connected environment.
Key Components of Industry 4.0

- The Internet of Things (IoT): Central to the rise of Industry 4.0, IoT enables physical objects, such as machines and sensors, to collect and share data. This real-time data flow helps companies optimize operations, reduce downtime, and predict maintenance needs.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI is transforming the way businesses function. With AI-driven algorithms, companies can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make smarter decisions. Machine learning, a subset of AI, allows systems to improve and learn from past experiences, pushing automation to new heights.
- Advanced Robotics: While robots have been a part of manufacturing for years, Industry 4.0 has introduced more sophisticated robots. These advanced robots can work alongside humans, adapt to new tasks, and even perform complex operations autonomously. They are more flexible, intelligent, and efficient than their predecessors.
- Big Data and Analytics: The rise of Industry 4.0 has made big data an invaluable asset. By analyzing large datasets, businesses can gain insights into customer behavior, production efficiency, and market trends. This data-driven approach allows for informed decision-making and helps companies stay ahead of the competition.
- Cyber-Physical Systems: These systems are the backbone of Industry 4.0, merging the physical and digital worlds. In a manufacturing context, machines and systems are interconnected through communication networks, enabling them to monitor and control physical processes in real-time.
- Cloud Computing: As the amount of data generated continues to grow, the need for scalable storage and processing power has become more apparent. Cloud computing allows companies to store vast amounts of data and access it from anywhere, promoting collaboration and flexibility.
The Benefits of Industry 4.0
The rise of Industry 4.0 is bringing a multitude of benefits to businesses across various sectors, especially manufacturing. Below are some of the key advantages:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation and real-time data analysis allow companies to streamline operations, reduce waste, and optimize production processes. This leads to lower costs and faster time-to-market for products.
- Improved Quality Control: With smart sensors and IoT devices, companies can monitor production lines in real-time, detecting defects early and ensuring consistent product quality. This minimizes errors and enhances customer satisfaction.
- Customization and Flexibility: Industry 4.0 enables manufacturers to offer more personalized products. By leveraging data and automation, companies can quickly adapt to changing consumer demands and produce customized goods without significant cost increases.
- Enhanced Supply Chain Management: The rise of Industry 4.0 has transformed supply chain management. With real-time data, companies can gain better visibility into their supply chains, predict disruptions, and respond quickly to challenges.
- Sustainability: By optimizing production and reducing waste, Industry 4.0 can contribute to more sustainable manufacturing practices. Companies can minimize resource consumption, lower their carbon footprint, and adopt eco-friendly methods.
- Job Creation and New Roles: While some fear that automation may lead to job losses, the rise of Industry 4.0 also creates new opportunities. As industries embrace new technologies, there is a growing demand for skilled workers in areas like data analysis, cybersecurity, and AI development.
Challenges in Implementing Industry 4.0
Despite the potential benefits, the rise of Industry 4.0 is not without challenges. Many companies, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), face hurdles in adopting new technologies. Some of the key challenges include:

- High Initial Investment: Implementing Industry 4.0 technologies requires a significant investment in new machinery, software, and infrastructure. For smaller businesses, these costs can be prohibitive, delaying adoption.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As more devices become connected, the risk of cyberattacks increases. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring the security of networks is a critical concern for companies looking to adopt Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Skill Gaps: The rise of Industry 4.0 demands a workforce with specialized skills in AI, robotics, data analysis, and cybersecurity. However, there is currently a gap between the skills required and those available in the job market. Bridging this gap will be crucial for the successful implementation of Industry 4.0.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many businesses still rely on legacy systems that may not be compatible with modern technologies. Integrating these older systems with new, interconnected technologies can be complex and costly.
The Global Impact of Industry 4.0
The rise of Industry 4.0 is not limited to manufacturing; its influence extends across various sectors, including healthcare, transportation, and agriculture. In healthcare, AI and big data are revolutionizing diagnostics and patient care. Smart farming, enabled by IoT devices and drones, is increasing agricultural productivity and sustainability. Autonomous vehicles, powered by AI and robotics, are reshaping the future of transportation.
Countries around the world are recognizing the importance of Industry 4.0 and are investing in initiatives to support its growth. Germany, a pioneer of the concept, continues to lead the charge with its “Industrie 4.0” strategy. Similarly, the United States, China, and Japan are making significant strides in adopting advanced technologies to stay competitive on the global stage.
The Future of Industry 4.0
As technology continues to evolve, the rise of Industry 4.0 will only accelerate. Emerging technologies like 5G, quantum computing, and blockchain will further enhance the capabilities of Industry 4.0 systems, enabling faster, more secure, and efficient operations.
Businesses that embrace this revolution will not only gain a competitive edge but also shape the future of industries worldwide. For those yet to adopt, the clock is ticking. The rise of Industry 4.0 is not just a trend—it’s the future.
Conclusion
The rise of Industry 4.0 marks a monumental shift in the way industries operate, bringing unprecedented levels of efficiency, customization, and innovation. While there are challenges to overcome, the benefits far outweigh the hurdles. Businesses that recognize and adapt to this new industrial revolution will be at the forefront of the global economy, driving progress for decades to come.
Found this article valuable? Explore more insights in our Enterprise Chronicles









