Have you ever wondered how much of our world is already run by machines? From self-driving cars to automated factories, the integration of robotics and automation is revolutionizing the way industries operate. No longer confined to science fiction, these technologies are becoming an essential part of modern-day businesses, improving efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. But what exactly is driving this rapid adoption across sectors?
What Are Robotics and Automation?
At their core, it refer to technologies that perform tasks typically carried out by humans, but with greater speed, precision, and repeatability. Robotics involves designing, building, and operating machines (robots) to carry out physical tasks, while automation refers to the use of control systems to handle processes with minimal human intervention.
The convergence of these two fields has led to transformative advancements in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, and logistics, offering solutions that streamline operations and reduce human error. Robotics and automation are not just reshaping the workforce; they are laying the foundation for future innovations that will define the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The Evolution of Robotics and Automation
They have evolved significantly since their inception. Initially, automation was confined to simple, repetitive tasks in manufacturing, such as assembly line work. However, advancements in technology, especially artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, have expanded the capabilities of robots and automation systems. Today, these technologies can perform complex tasks like real-time decision-making, predictive maintenance, and autonomous navigation.
The earliest robots were mechanical arms used in factories for welding and assembly. Now, robots are capable of interacting with their environment, adapting to changes, and even learning from their experiences. Automation systems, once restricted to basic functions, now control entire production lines, optimize workflows, and even manage supply chains.
Applications of Robotics and Automation in Industries
1. Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry has been a primary beneficiary of it. Automated systems have revolutionized production lines by increasing speed and reducing the margin for error. Robots handle everything from assembly to quality control, and they can operate 24/7 without the need for breaks or shifts. These technologies have significantly reduced operational costs, allowing companies to meet higher production demands while maintaining quality standards.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, robotics and automation are improving patient care and streamlining operations. Surgical robots, for example, assist doctors in performing minimally invasive procedures with greater precision. Automation is also making its way into administrative tasks, such as patient record management and appointment scheduling. These technologies are helping healthcare providers focus more on patient care, reducing the time spent on routine tasks.
3. Agriculture
Agriculture is another sector where robotics and automation are making a profound impact. Automated machinery can plant, monitor, and harvest crops with greater efficiency than human labor. Drones equipped with sensors can monitor crop health, while autonomous tractors and harvesters reduce the need for manual labor. This not only boosts productivity but also enables farmers to make data-driven decisions about their operations.
4. Logistics and Supply Chain
The logistics industry is experiencing a seismic shift due to robotics and automation. Automated warehouses use robots to pick, pack, and ship goods, reducing delivery times and human error. Self-driving trucks and drones are being tested for last-mile delivery, promising to further enhance the efficiency of supply chains. They are also helping companies manage inventory more effectively, ensuring that stock levels are optimized and products are delivered on time.
The Role of AI in Robotics and Automation
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in advancing them. With AI, machines can go beyond pre-programmed instructions and adapt to changing environments. They can learn from data, recognize patterns, and make decisions in real time. AI-powered robots are becoming smarter and more autonomous, capable of performing complex tasks such as diagnostics in healthcare or predictive maintenance in industrial settings.
For example, AI-driven robots in manufacturing can detect defects in real-time, ensuring quality control without halting production. In logistics, AI optimizes routes for autonomous vehicles, reducing fuel consumption and delivery times. By combining AI with them, industries can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, allowing machines to make intelligent decisions without human intervention.
Benefits of Robotics and Automation
1. Increased Productivity
One of the most significant advantages of this is the boost in productivity. Machines can work continuously without fatigue, drastically increasing output. In industries like manufacturing, this has led to faster production cycles and higher output levels. Automated systems are also less prone to errors, ensuring consistency in quality and reducing waste.
2. Cost Efficiency
While the initial investment in robotics and automation technology can be high, the long-term savings are substantial. Automated systems reduce the need for manual labor, lower the chances of human error, and cut down on production costs. Businesses can also operate round the clock, eliminating the need for overtime pay or extra shifts.
3. Improved Accuracy and Precision
They excel in performing tasks that require high precision and accuracy. For instance, in medical surgeries, robotic systems can carry out delicate procedures with minimal risk of error. In manufacturing, automated machinery ensures uniformity in products, which is essential for industries like electronics and automotive manufacturing.
4. Enhanced Safety
In industries like mining, construction, and chemical manufacturing, robotics and automation have significantly improved safety. Machines can be used to perform dangerous tasks, reducing the risk of injury to human workers. This not only protects the workforce but also reduces liability for companies.
Challenges Facing Robotics and Automation
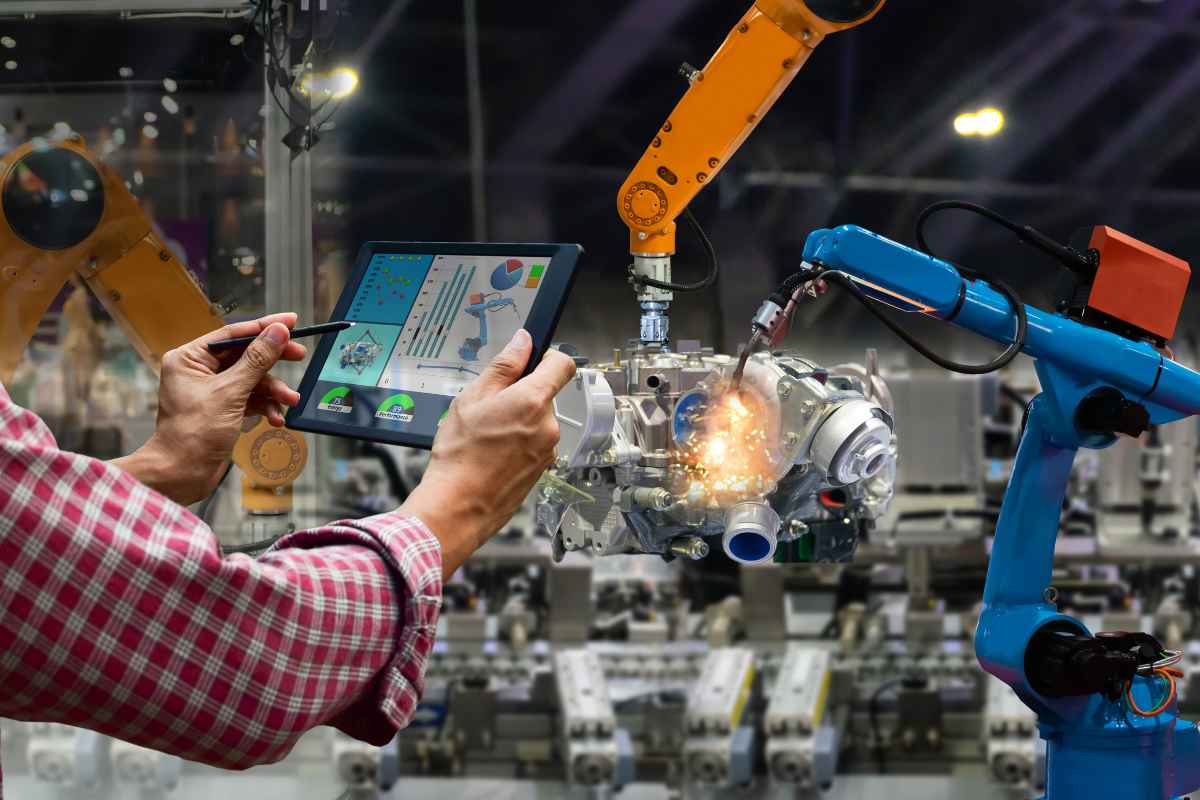

Despite the numerous benefits, the widespread adoption of robotics and automation comes with challenges. One of the main concerns is the displacement of human labor. As machines take over more tasks, the demand for human workers in specific industries decreases. This has raised concerns about job loss and the need for workers to reskill or transition to other fields.
Another challenge is the high cost of implementation. While robotics and automation can lead to long-term savings, the initial setup costs can be a barrier for smaller businesses. Additionally, the integration of these systems into existing workflows can be complex, requiring significant changes to infrastructure and processes.
Found this article valuable? Explore more insights in our Enterprise Chronicles.
The Future of Robotics and Automation
The future of robotics and automation is filled with exciting possibilities. As technology continues to advance, machines will become even more intelligent, autonomous, and capable of interacting with their environment in more sophisticated ways. Robotics and automation will likely extend into new sectors, such as education, retail, and customer service, revolutionizing the way we live and work.
In the coming years, we can expect to see greater collaboration between humans and robots, with machines taking over repetitive and dangerous tasks, while humans focus on more creative and strategic roles. This shift will require a change in the workforce, with an emphasis on digital skills and adaptability.
Robotics and Automation in Everyday Life
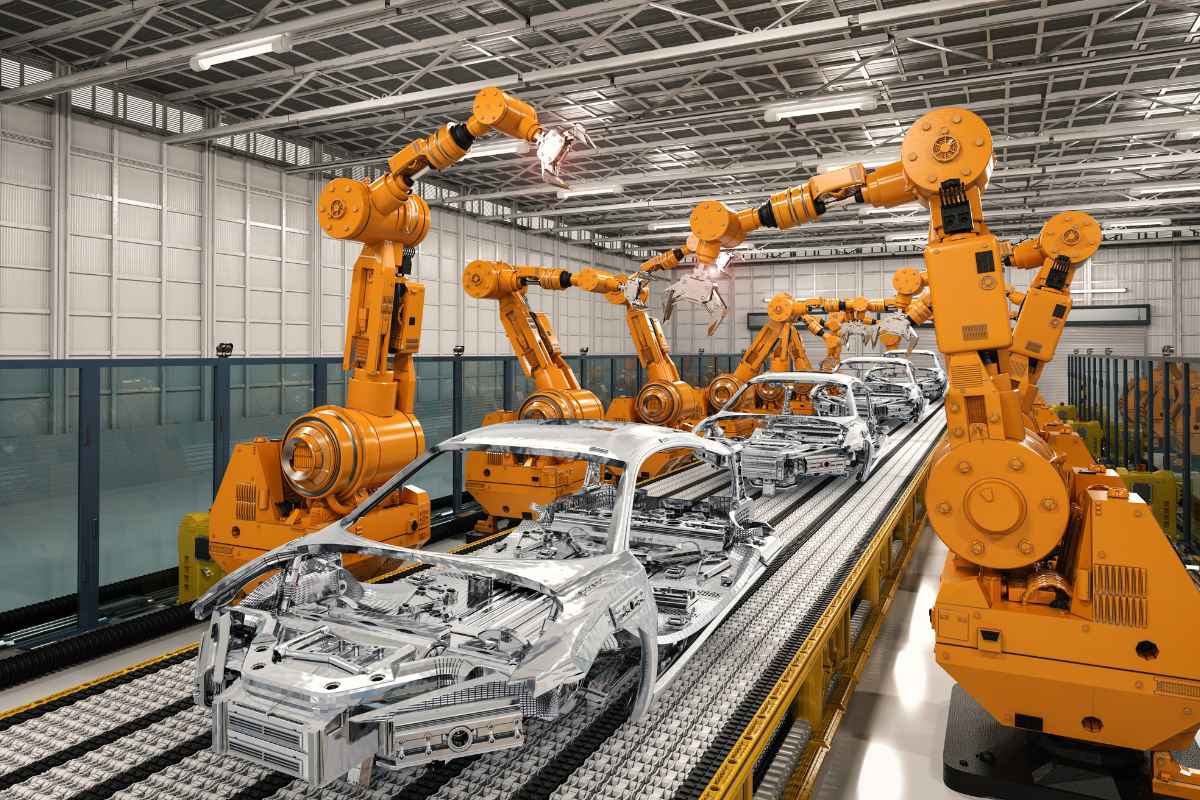

While they have primarily been associated with industries like manufacturing and logistics, their impact is becoming increasingly visible in everyday life. From robotic vacuum cleaners to smart home systems, automation is making daily tasks more convenient and efficient.
In retail, for example, automation is being used to manage inventory, process payments, and even assist customers through AI-powered chatbots. In the transportation industry, self-driving cars and drones are becoming more common, promising to reshape the way we commute and deliver goods. Robotics and automation are no longer limited to industrial use but are becoming integral to how we live, shop, and interact with technology.
The Ethical Considerations of Robotics and Automation
As they become more advanced, ethical considerations around their use are becoming more pressing. One of the main concerns is the potential for job displacement. While automation can create new jobs in tech and engineering, it can also render certain roles obsolete, particularly in industries that rely heavily on manual labor.
There are also concerns about privacy and security, especially as AI-powered robots and automated systems collect and process vast amounts of data. Ensuring that these technologies are used ethically and that appropriate safeguards are in place is essential to preventing misuse.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation are not just buzzwords; they are driving forces behind the modern industrial revolution. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will reshape industries, create new opportunities, and improve efficiency across the board. While challenges like job displacement and ethical concerns need to be addressed, the benefits of robotics and automation are undeniable.
Businesses and industries that embrace robotics and automation will be better positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive and technology-driven world. The future is bright for robotics and automation, and their role in shaping the next generation of industries is only just beginning.









